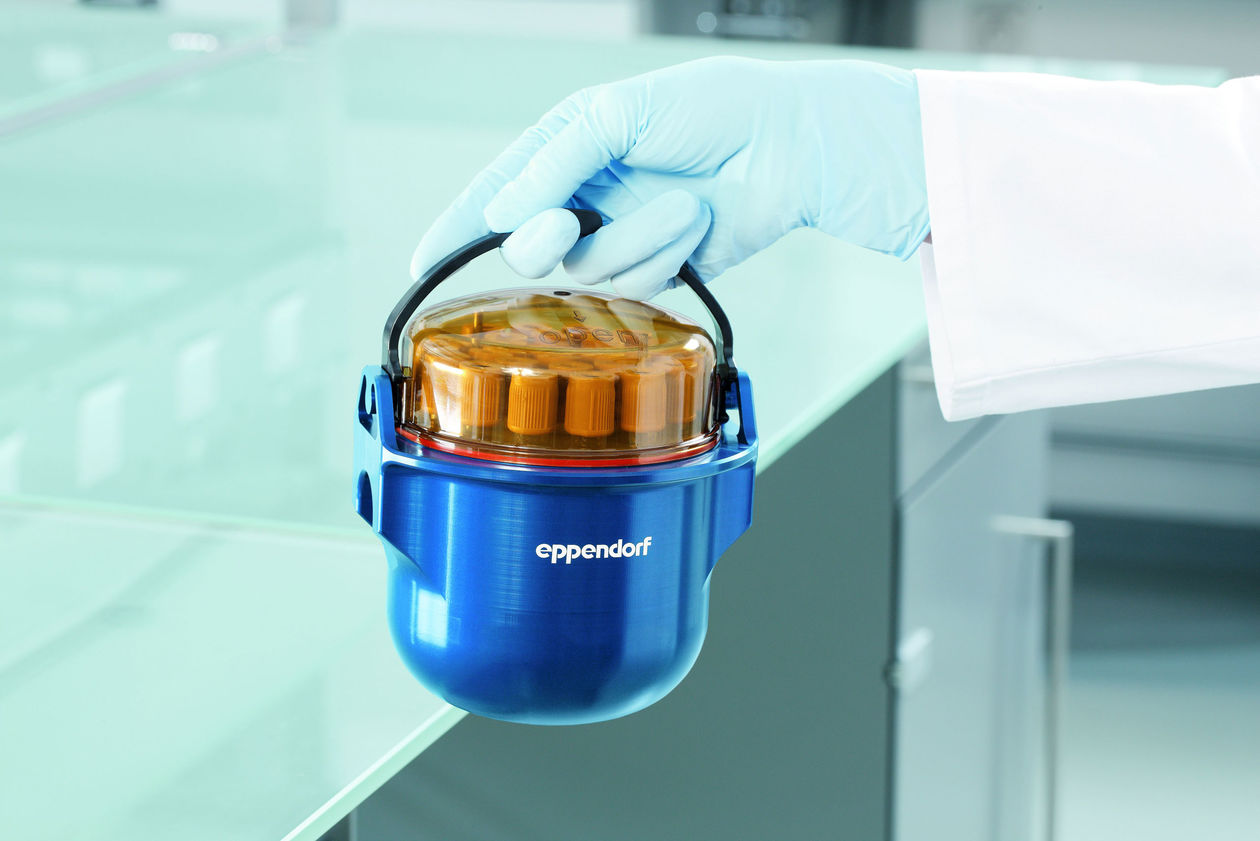
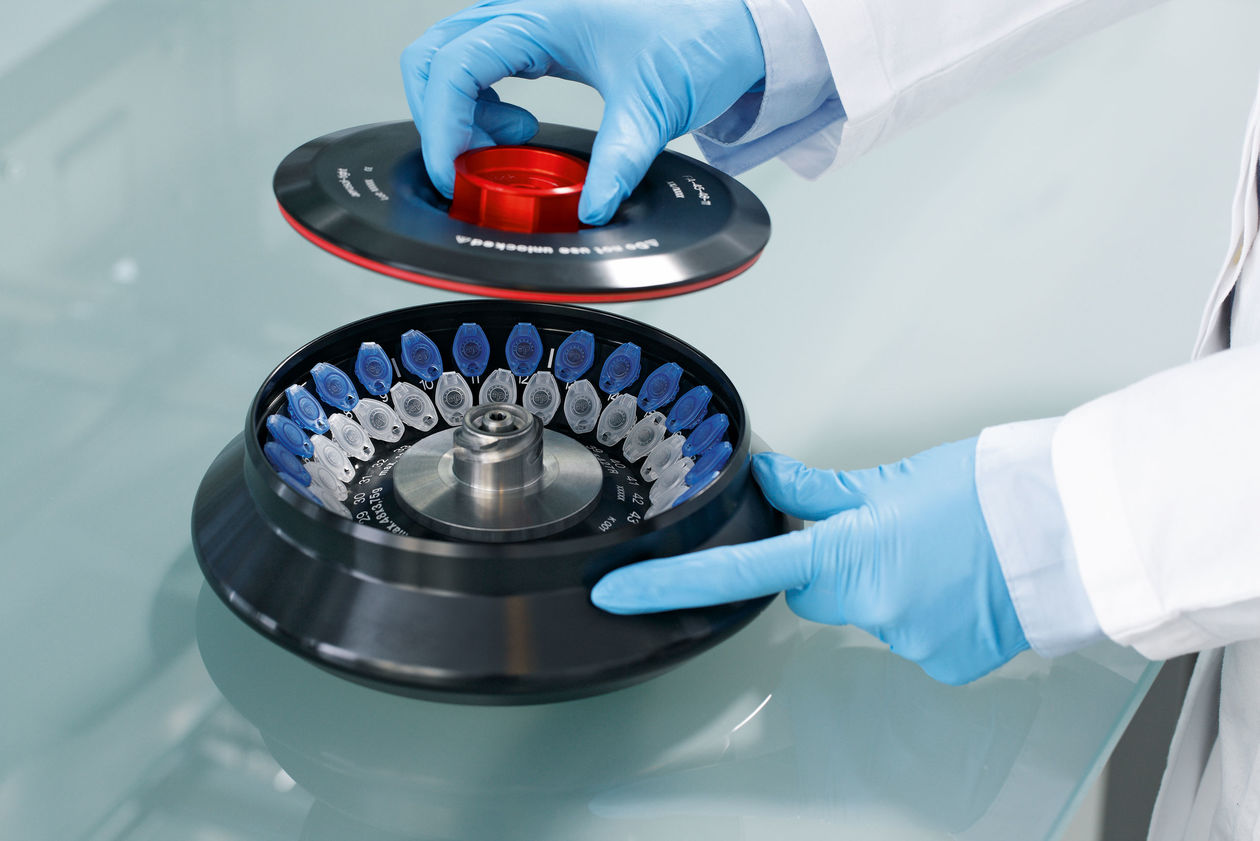
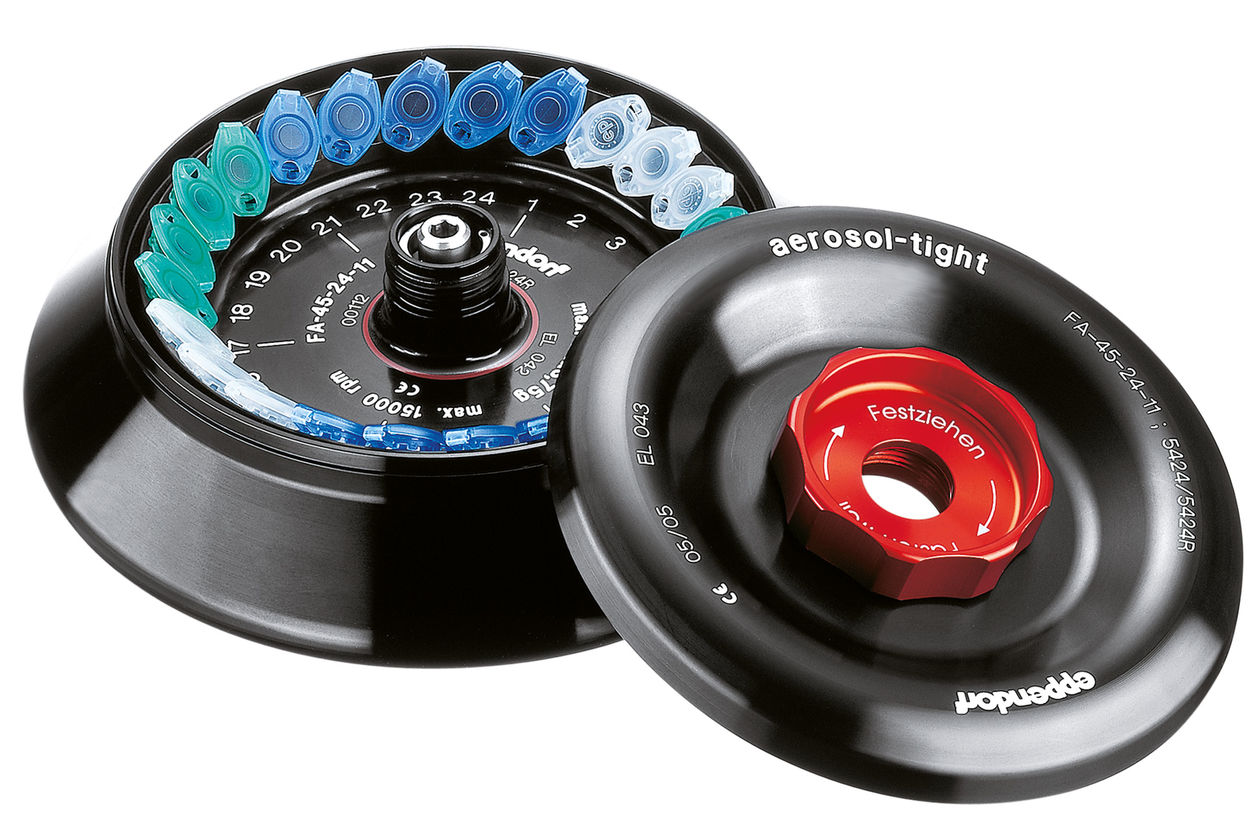
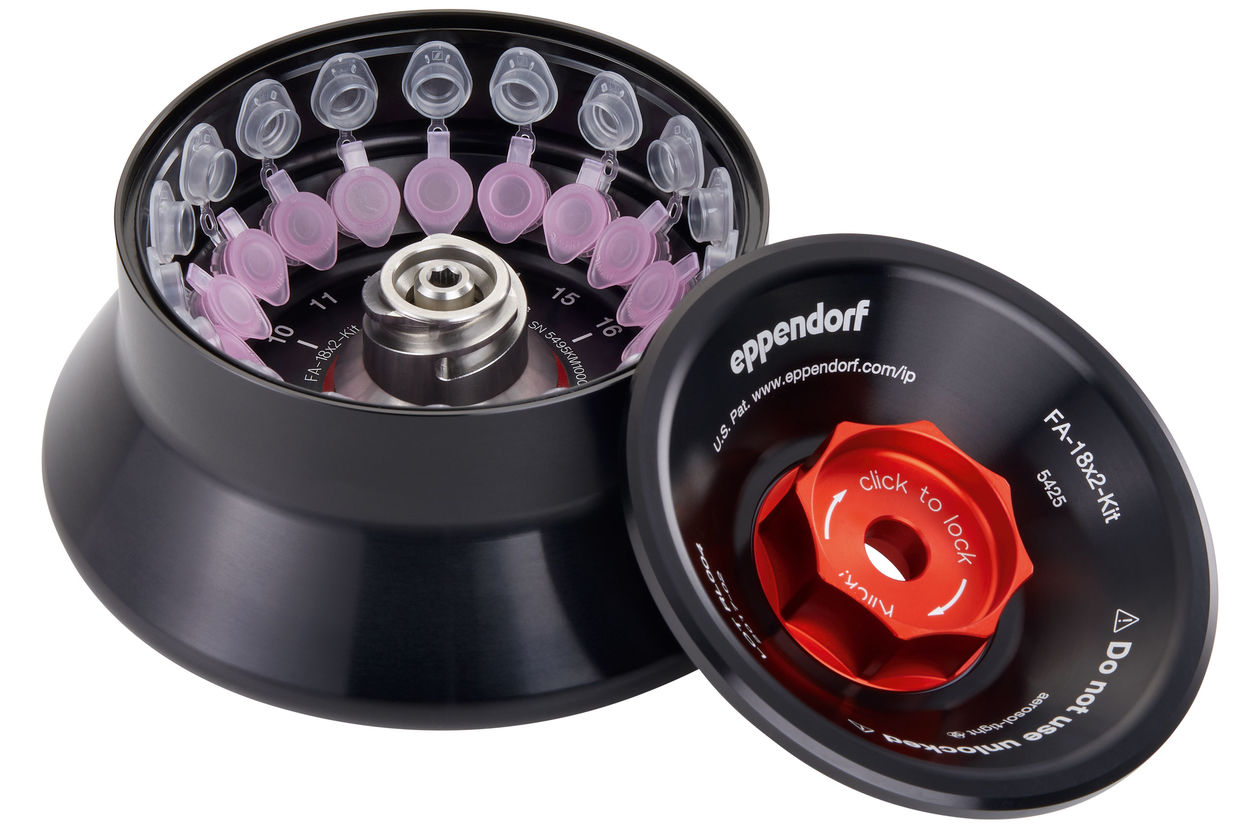
Handling infectious microorganisms like SARS-CoV-2 in research laboratories or vaccine development could lead to laboratory acquired infections. According to preliminary research, the novel SARS-CoV-2 virus is likely to survive in the air for several hours in aerosols (more precisely bioaerosols), thus playing a critical role in your laboratory safety measures. To ensure the safety of laboratory personnel and to prevent laboratory acquired infections, reasonable precautions must be taken throughout the whole workflow. This includes centrifugation steps as centrifuges can be a source of bioaerosols. Here we provide information how to centrifuge potentially infectious samples.