MENU
BR | BRL
BR | BRL
-
- Centrífugas de bancada
- Centrífugas de piso
- Centrífugas refrigeradas
- Microcentrífugas
- Centrífugas multiúso
- Centrífugas de alta velocidade
- Ultracentrífugas
- Concentrator
- High-Speed and Ultracentrifuge Consumables
- Tubos de centrífuga
- Placas de centrífuga
- Gerenciamento de dispositivo
- Gerenciamento de amostras e informação
-
- Pipetagem manual & dispensação
- Pipetas mecânicas
- Pipetas eletrônicas
- Pipetas multicanal
- Pipetas de deslocamento positivo e dispensadores
- Sistema automatizado de Pipetagem
- Dispensadores de bancada
- Controladores de pipeta
- Ponteiras de pipeta
- Consumíveis de automação
- Acessórios para pipetas e dispensadores
- Acessórios de automação
- Serviços para pipetas e dispensadores
Sorry, we couldn't find anything on our website containing your search term.
Extracellular Vesicle/Exosome Production
Extracelluar vesicles (EVs) such as exosomes are secreted by cells and can transport molecular payloads, such as proteins or genetic material, between cells. In doing so, they have the ability to modulate cell communication, immune regulatory processes, tumor metabolism, and regenerative/degenerative processes. Extracellular vesicles have recently become of great interest for their use as therapeutic and diagnostic tools. The ever-greater need for industry-scale EV/exosome production requires process development efforts to meet the demands of research and development projects. The use of stirred-tank bioreactors for upstream expansion represents one of the best approaches to ensuring optimal EV/exosome production conditions and enabling tight monitoring and control of the bioprocess in a highly scalable setup. The use of centrifuges is considered the gold standard for the purification of extracellular vesicles from the culture medium.
Read more
Read less
Strategies for large-scale EV/exosome production
Now gaining traction, the use of extracellular vesicles such as exosomes for cell and gene therapy applications is increasingly reliant upon the production of high amounts of high-quality vesicles. As with every cell culture process, the EV/exosome upstream expansion workflow presents numerous opportunities to introduce variability, and this can lead to poor yield and batch inconsistencies. In comparison with conventional 2D culture platforms, bioreactors offer numerous advantages to control the cells’ growth environment and increase the working volume. Like this they are valuable tools for process development to produce EVs/exosomes in a scalable and reproducible manner.
Read more
Read less
How are exosomes utilized in the cell and gene therapy field?
Gene therapy vectors
Since exosomes are natural molecule transporters, they are well suited to carrying nucleic acids. With a robust membrane to prevent degradation, good stability, low immunogenicity, plus the rapid nature by which they are taken up by target cells, exosomes bring value to the CGT field with unique advantages as gene therapy vectors. One of the stand-out benefits of exosomes as advanced therapy vectors is their wide tropism. This describes their ability to infiltrate a large variety of cell and tissue types thanks to their ability to cross biological barriers such as the blood brain barrier and cytoplasmic membranes. This makes exosome vectors an attractive option for the treatment of diseases where pathology occurs in difficult-to-access tissues, like the central nervous system. Traditional therapeutics are often unable to access such areas, but the broad tropism of exosomes enables researchers to transport specialized therapies, where needed, to provide novel treatment options. The majority of exosome-based gene therapy applications aim to treat cancers or neurological diseases.
Read more
Read less
Regenerative medicine
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy is a popular technique used in regenerative medicine, in which MSCs engraft into injured tissue and promote regeneration. Due to the low MSC survival in the host tissue during MSC cell therapy though, recent evidence indicates that the MSC’s secretome (the total set of proteins known to be released MSCs) could be central to their benefits in tissue regeneration. Exosomes make up a large part of the MSC secretome, and their ability to deliver proteins and genetic material while mediating the immune response makes exosomes a promising cell-free therapy for regenerative medicine. MSC-derived exosomes have demonstrated promise in a versatile range of regeneration therapies from bone and cartilage to neuronal regeneration, and research into exosomes for cell free regenerative therapy looks set to continue to grow in popularity.
Read more
Read less
Exosomes have several advantages over cells as a tool for regenerative medicine. To name a few:
- Non-immunogenic: Exosomes are less likely to be recognized as foreign by the recipient's immune system compared to cells, which can trigger an immune response and lead to rejection. This makes exosomes a safer and more viable option for allogeneic transplantation.
- Stable and easy to store: Exosomes are small and stable, which makes them easier to store and transport compared to cells, which require specific storage conditions and may have a limited shelf life.
- Targeted delivery: Exosomes can be engineered to target specific tissues or cells, which makes them a more precise tool for delivering therapeutic payloads compared to cells, which may not be able to target specific tissues or may migrate away from the site of injury.
- Cost-effective: Producing exosomes is often less expensive than producing cells, which makes exosomes a more cost-effective option for large-scale clinical use.
- Lower risk of tumorigenesis: Exosomes do not have the potential to form tumors, which is a risk associated with cell-based therapies.Due to this another potential advantage of exosomes from a regulatory point of view is that they may be subject to less stringent regulations compared to cells or tissues, as they are considered to be a subset of cells and not a distinct product. However, this may vary depending on the intended use ofthe exosomes and the regulatory requirements in different countries.
Read more
Read less
Discover our products for extracellular vesicle production
Discover our bioreactor control systems and centrifuges for extracellular vesicle process development, scale-up of EV production, and EV purification.
Read more
Read less
Incubators for the pre-culture of cells
A preculture step is usually required to expand the cells used for extracellular vesicle production. In this step, the cell quantities needed to create a cryopreserved cell bank and to inoculate the culture in the bioreactor are achieved.
Read more
Read less
CellXpert® C170i
- CO2 incubator for static culture of cells, typically in T-flasks or dishes
- Easy cleaning and disinfection with seamless chamber, easy disassembling in 40 s, removable water tray and 180 °C disinfection with protocol
- GMP-/Cleanroom-related certificates & features

Bioreactors for process development and small-scale production
Extracellular vesicle production at small-scale is an important first step for researchers seeking to optimize their process prior to scale-up. Bioreactors’ process monitoring and control capabilities can standardize culture conditions in the upstream process, and ensure that the EV-producing MSCs are maintained at optimum conditions. In turn, this reproducible production workflow makes for a high quality, high yield EV production.
Read more
Read less
DASbox® Mini Bioreactor System
- Working volume range: 60 mL to 250 mL
- Parallel processing of up to 24 bioreactors
- Perfect tool to support the process development, through identifying the most appropriate cell culture parameters required for exosome production before scaling-up.

Want to discover how the DASbox® Mini Bioreactor System can be harnessed for small scale extracellular vesicle production? Check out our application note!
Read more
Read less
Bioreactors for scaling up extracellular vesicle production
To scale-up extracellular vesicle production from the benchtop to production scale, larger-scale bioreactor systems that can support a large number of cells is central to success. One such solution that can support this is the SciVario® twin bioreactor control system from Eppendorf.
Read more
Read less
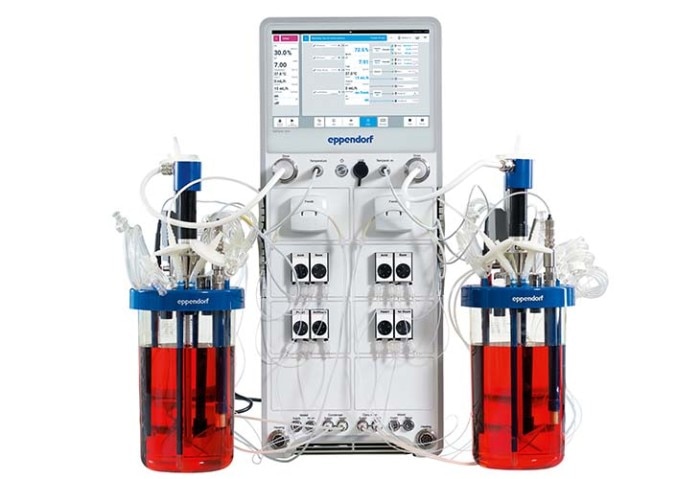
SciVario® twin bioreactor control system
- Working volume range: 1.25 L to 40 L
- Can control two bioreactors independently
- Has been demonstrated to be a powerful tool in the medium to large scale production of extracellular vesicles

To characterize the extracellular vesicle production process, it is sometimes helpful to take small samples from the bioreactor and further cultivate them in shake flasks in a CO2 shaker in parallel to the main culture. One solution to support this is the New Brunswick S41i CO2 shaker.
Read more
Read less
New Brunswick S41i
- Integrated platform for parallel static cultivation of T-flasks, dishes or plates
- Shake flask range: 10 mL to 5 Liter Corning® or Thomson flasks
- Integrated high temperature disinfection cycle
- Can be used in EV scale-up and collection process

Researchers used the SciVario® twin to produce favorable conditions for cellular growth, viability and metabolic activity, and extracellular vesicle production. To quantify extracellular vesicle production at different time points of the bioprocess run, cell samples were transferred to a New Brunswick S41i CO2 shaker where they were cultivated in a different medium than the main culture. Find out in our application note, how the SciVario® twin and the New Brunswick S41 supported extracellular vesicle production!
Read more
Read less
Centrifuges for the purification of extracellular vesicles
After production, the extracellular vesicles are purified from other components in the culture medium. Centrifugation is a versatile method and nowadays the gold standard in the field.
Read more
Read less
High-Speed Centrifuge CR22N - For clearance of culture medium
- High-speeds of up to 58,700 x g are ideal for clearance of cells, cell debris, and microvesicles from cell media, as the first step in exosome purification
- Rotor R15A can in a single run accommodate up to 650 mL of cell media in 15 mL and 50 mL high-speed conical tubes, speeding up processing to less than1 hour. Larger volumes up to 1.5 L per sample are available
- The device offers user management and documentation function to support users with GxP compliance

Ultracentrifuge CP100NX - For pelleting extracellular vesicles
- Swing-bucket rotor P32ST allows pelleting exosomes in 6 x 40 mL tubes in only 90 min
- Even higher speeds up to 803,000 x g with rotor P100AT2 and capacities of up to 1,380 mL with rotor P21A2 can be reached
- The device offers user management and documentation function to support users with GxP compliance

Find out more in our application note on how Centrifuge CP100NX and Centrifuge CR22N are the perfect complement to purify your extracellular vesicle products after the bioprocess run. Download application note!
Find out more about the collection of exosomes from blood! Download protocol!
Find out more about the collection of exosomes from blood! Download protocol!
Read more
Read less
Contact us
Are you interested in cultivating extracellular vesicle-producing cells? Please contact us to discuss the needs of your individual application.
Read more
Read less
Eppendorf bioprocess solutions for your applications
Visit our main bioprocessing website to discover our bioprocess solutions for various industries and applications.
Read more
Read less